Creative professionals are increasingly surrounded by tools that promise speed, scale, and efficiency. At the same time, many designers, marketers, and content creators worry that automation risks flattening ideas, diluting authorship, or replacing judgment with convenience. AI agents, when used thoughtfully, offer a different path. Rather than automating creativity itself, they can support the process around creative work, freeing humans to focus on taste, narrative, and decision-making.
This article explores how to build creative workflows with AI agents in a way that strengthens, rather than undermines, human creativity.
What “Agentic AI” Means in a Creative Workflow
Most creative professionals are already familiar with single-prompt AI use: asking a tool to generate copy, suggest ideas, or summarize research. Agentic AI goes a step further.
An AI agent is a role-driven system designed to pursue a goal over multiple steps. In a creative context, this means assigning distinct responsibilities to AI agents that mirror how creative teams already work.
For example:
- One agent explores possibilities and expands ideas.
- Another evaluates alignment with a brief or brand.
- A third refines language, structure, or presentation.
The key shift is not intelligence, but orchestration. AI agents operate within a framework designed by humans, with clear boundaries and checkpoints.
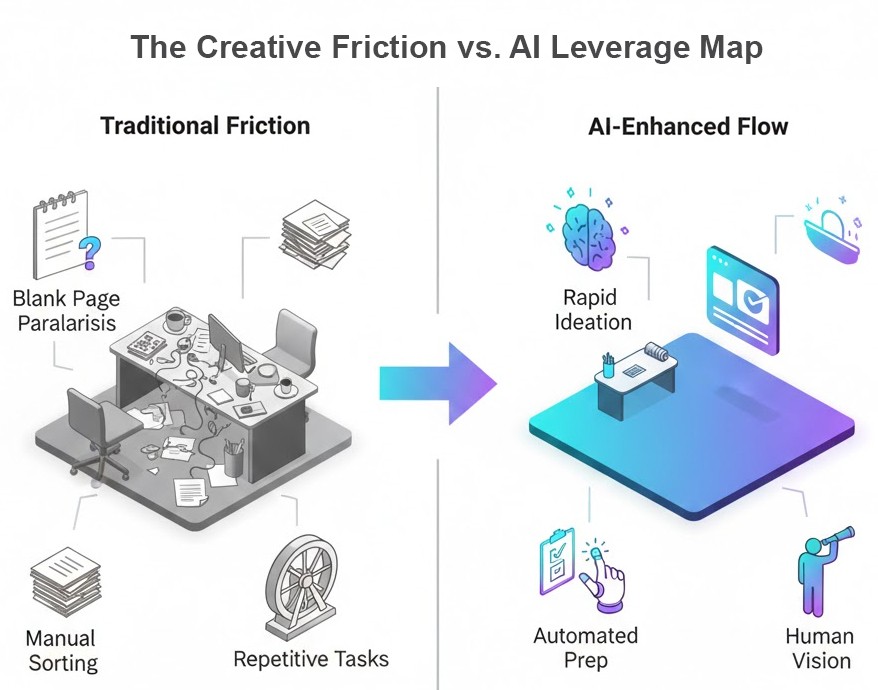
Why AI Agents Are Useful for Creative Professionals
Creativity rarely fails because of a lack of ideas. It fails because of friction: blank-page paralysis, scattered inputs, time spent on low-leverage tasks, or difficulty exploring alternatives under deadlines.
AI agents are particularly effective at:
- Expanding idea space without exhausting the creator
- Automating preparatory or repetitive work
- Acting as a structured “second brain” during exploration
- Supporting collaboration across disciplines
When used correctly, they increase optionality, not conformity.
High-Leverage Use Cases Across Creative Disciplines
Brainstorming and Ideation
AI agents excel at divergent thinking. They can rapidly generate multiple angles, metaphors, or creative directions based on a brief, allowing humans to select and refine rather than invent from scratch.
Use agents to:
- Explore alternative concepts
- Stress-test early ideas
- Generate contrasting approaches for comparison
Well-suited tools and platforms:
- ChatGPT / Claude / Gemini – for structured brainstorming, reframing prompts, and concept expansion
- Grok – useful for fast, opinionated takes and unconventional angles
- Notion AI / Obsidian with AI plugins – for capturing, clustering, and evolving ideas over time
- Miro with AI features – for visual brainstorming and mapping idea relationships
Human judgment remains essential in deciding what is original, appropriate, and valuable.
Branding and Visual Identity
In branding projects, AI agents can support the exploratory phase without dictating outcomes, helping teams move from abstract strategy to tangible creative directions.
Examples include:
- Generating naming directions based on brand attributes
- Translating abstract values into visual language
- Drafting mood board themes or style descriptors
Well-suited tools and platforms:
- ChatGPT / Claude – for brand positioning language, naming logic, and tone-of-voice exploration
- Figma (with AI features) – for early visual ideation, layout exploration, and design iteration
- Midjourney / DALL·E – for mood boards, visual metaphors, and aesthetic exploration (not final assets)
- Adobe Firefly – for brand-safe visual experimentation within design workflows
These outputs are starting points. Final brand decisions should always reflect human taste, cultural awareness, and strategic intent.
Photography and Visual Production
For photographers and visual storytellers, AI agents can assist before and after the shoot, without interfering with the act of image-making itself.
Practical applications include:
- Shot list ideation aligned with a narrative goal
- Location or lighting concept exploration
- Post-shoot curation logic (grouping, sequencing, selection criteria)
Well-suited tools and platforms:
- ChatGPT / Claude – for conceptual planning, storytelling structure, and shot logic
- Midjourney / DALL·E – for pre-visualization and conceptual mood references
- Adobe Lightroom (AI features) – for culling, tagging, and pattern recognition across large sets
- Capture One (with AI tools) – for professional-grade workflow support and image organization
The camera, composition, and decisive moment remain human. The agent supports planning and reflection, not authorship.
Marketing and Content Systems
In marketing and content creation, AI agents are especially valuable for structure, consistency, and scale across channels.
They can help with:
- Topic clustering and content planning
- Campaign ideation across channels
- Drafting variations for testing and refinement
- Repurposing long-form content into multiple formats
Well-suited tools and platforms:
- ChatGPT / Claude – for long-form drafting, content repurposing, and editorial refinement
- Gemini – particularly useful when working across Google Docs, Sheets, and search-driven workflows
- Surfer SEO / Clearscope – for AI-assisted SEO structure and topic coverage
- Notion / ClickUp with AI – for coordinating briefs, approvals, and content pipelines
Used properly, this reduces manual overhead while preserving editorial voice and strategic coherence.
Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration Tools
Where AI agents add the most value: alignment across roles and reduced coordination overhead.
Best Tool Categories & Examples
- AI-enhanced project management platforms
For translating creative intent into tasks and timelines. - Documentation and knowledge-base tools with AI search
For preserving decisions, rationale, and creative history.
Human-in-the-loop reminder:
AI can clarify and connect, but it cannot replace shared understanding or trust.
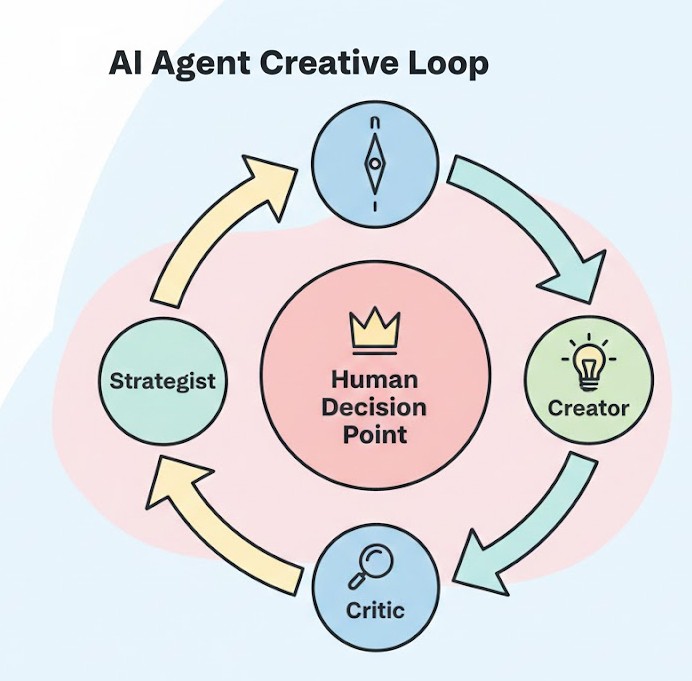
Designing a Simple Agent-Based Creative Workflow
A practical way to start is by modeling agents after familiar creative roles.
Example: Content or Campaign Development Workflow
- Strategist Agent
Clarifies objectives, audience, constraints, and success criteria. - Creative Agent
Generates multiple concepts, angles, or narratives aligned with the brief. - Critic Agent
Evaluates ideas for clarity, differentiation, and alignment with goals. - Human Decision Point
Selects, refines, or discards ideas based on taste, context, and intuition.
This structure mirrors how creative teams already work. The difference is speed and scale, not authorship.
Guardrails: Where Creative Teams Go Wrong with AI Agents
The most common risks are not technical, but conceptual.
- Homogenization
Over-reliance on AI outputs can lead to generic ideas if human filtering is weak. - Over-Automation
Automating creative decisions, rather than preparation or exploration, erodes quality. - Loss of Ownership
If no one feels responsible for the final outcome, the work suffers. - Ethical and IP Concerns
Creators must remain aware of originality, sourcing, and proper attribution. For instance, when using AI for visual mood boards, ensure you’re not inadvertently recreating copyrighted styles or imagery.
AI agents should support creative thinking, not replace accountability.
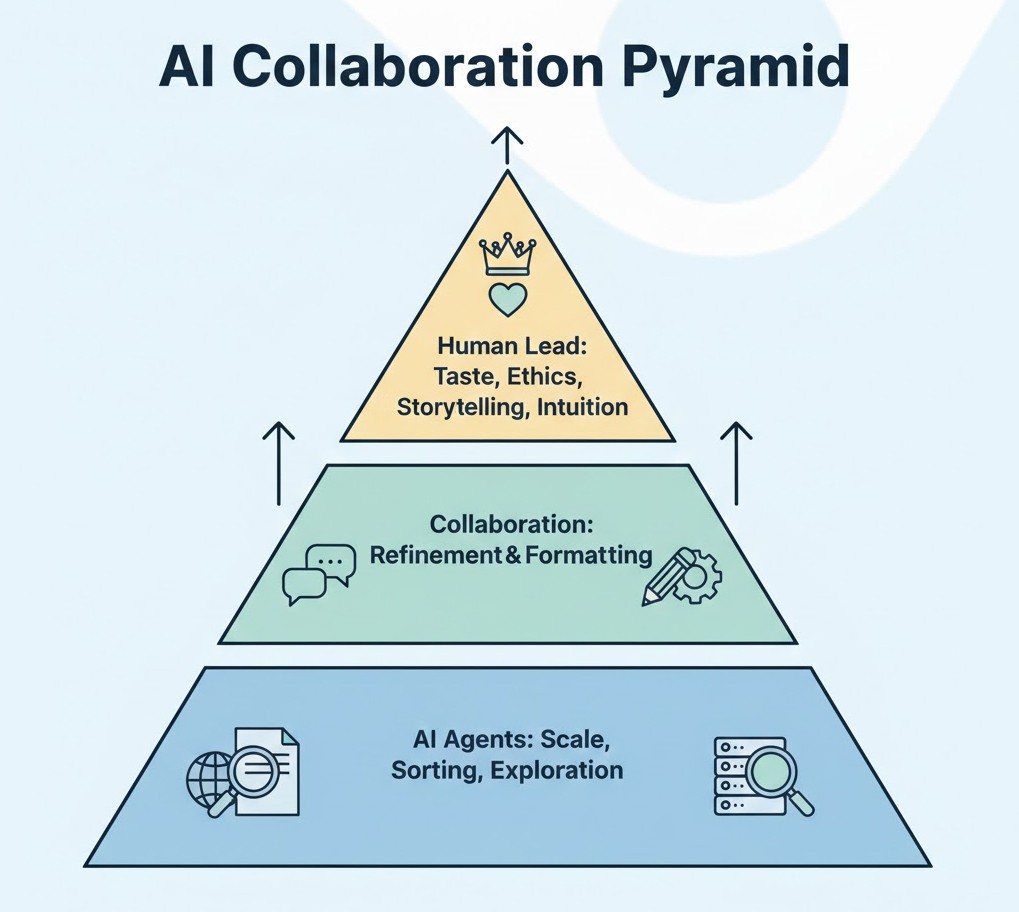
Best Practices for Human–AI Creative Collaboration
- Use AI agents early in the process, not at the final decision stage.
- Treat outputs as raw material, not finished work.
- Define explicit human checkpoints in every workflow.
- Periodically audit results for sameness or drift.
- Avoid using AI when intuition, emotional nuance, or lived experience is central.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Mistake: Using the same agent or prompt structure for every project
Creative work varies by context, audience, and medium. Reusing identical agent roles or prompts leads to predictable outputs and limits exploratory depth. Each project should redefine agent responsibilities based on the creative challenge.
Mistake: Failing to document what the AI contributed versus human decisions
When roles are unclear, ownership erodes. Teams should explicitly track which ideas were machine-generated and which were selected, refined, or rejected by humans. This preserves authorship and improves future workflow design.
Mistake: Allowing AI outputs to skip human critique stages
Bypassing review checkpoints in the name of speed often results in generic or misaligned work. AI should accelerate exploration, not short-circuit judgment.
Creativity is not just about producing options; it is about choosing the right ones.

A Practical Template to Get Started
Creative Workflow with AI Agents
Project Goal:
Develop a campaign concept for a mid-market SaaS brand launching a new analytics feature.
Human Lead:
Creative Director / Content Strategist
Agent Roles and Time Allocation:
- Strategist Agent (15–20 minutes)
Defines audience, objectives, constraints, and success metrics.
Decision criteria: Does the brief clearly articulate who this is for and why it matters? - Creative Agent (30–40 minutes)
Generates multiple concept directions, narratives, or visual themes.
Decision criteria: Are ideas distinct, non-obvious, and aligned with brand tone? - Critic Agent (15 minutes)
Evaluates concepts for clarity, differentiation, and feasibility.
Decision criteria: Which concepts balance originality with strategic fit? - Human Decision Point (Unlimited, but deliberate)
Selects one or two directions to refine, discard, or combine based on taste, context, and experience.
Documentation Check:
- AI-generated inputs logged
- Human-selected and modified elements noted
- Final authorship clearly attributed
This structure ensures AI accelerates thinking while humans remain accountable for meaning, quality, and direction.
The Strategic Advantage Going Forward
As AI tools become more capable, the differentiator will not be access to technology, but the ability to use it with discernment. Taste, judgment, storytelling, and ethical responsibility remain human strengths.
AI agents are most powerful when they operate quietly in the background, amplifying creative capacity without claiming authorship. For professionals working at the intersection of tech, business, and creativity, the goal is not to work faster at any cost, but to work better, with systems that respect both efficiency and originality.
Used wisely, AI agents can become trusted collaborators in creative workflows, enabling professionals to focus on what matters most: making meaningful, distinctive work.












