Buying property abroad is an exciting step, but the way mortgages are structured outside the US can be quite different. International lenders often follow their own rules and priorities, which means you’ll face processes that don’t always match what you’re used to back home.
To make smart decisions, you need to understand these differences clearly. Keep reading to see how international mortgages compare with US loans so you’ll know what to expect.
Understanding International Mortgages
An international mortgage is designed for non-residents or foreign nationals buying property outside their home country. These loans are often tailored to handle complex income sources, foreign currency, and cross-border regulations. In contrast, US loans usually follow set guidelines defined by domestic lenders and government-backed entities like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
While the US market offers relatively standardized products, international options can vary dramatically from one country to another. That’s where specialist advice becomes essential. If you’re exploring property outside the States, you may come across terms like US international mortgages, which are solutions specifically designed to connect US buyers with overseas opportunities.
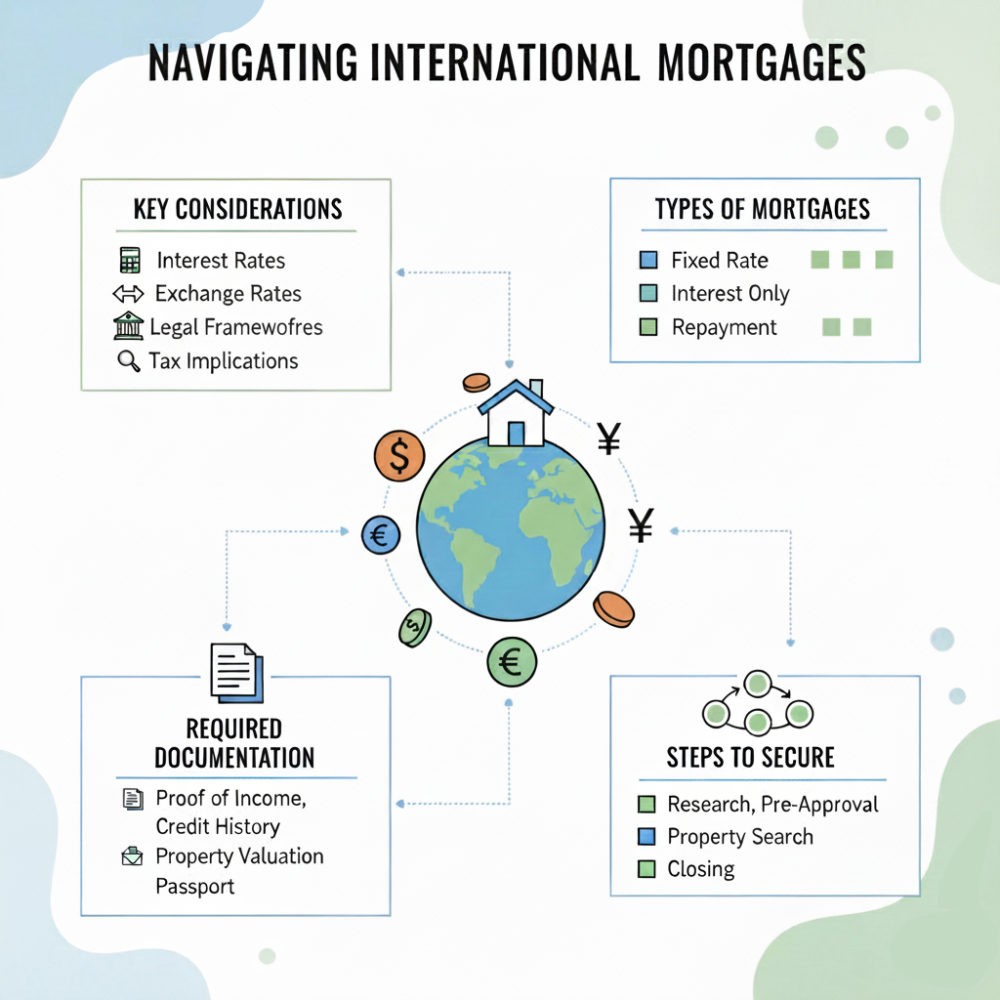
Loan Structures and Rules
One of the biggest differences lies in loan structures. In the US, fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages dominate the market, with 15- and 30-year terms being common. Lenders often focus on credit scores and debt-to-income ratios to determine eligibility.
International mortgages, however, rarely follow the same formula. Many overseas lenders base their assessments more on income, residency status, or local regulations. Some countries set a lower loan-to-value ratio than the US, requiring a larger upfront deposit. For instance, conventional US mortgages often allow LTV ratios up to 80-97%, enabling down payments as low as 3-20%. In contrast, international mortgages for non-residents typically range from 50-80% LTV, requiring 20-50% down payments, with some European and Asian lenders capping at 70% for foreign buyers.
Currency and Payment Considerations
Another clear distinction is how payments are handled. In the US, loans are paid in dollars, with predictable monthly installments. International mortgages often require payments in the local currency, which exposes borrowers to exchange rate risk. Even small fluctuations can significantly affect your repayment amount.
Some lenders also demand that you hold a local bank account, which adds another step to the process. These extra requirements highlight the importance of financial planning before committing to an overseas property loan.
Legal and Property Rights Differences
Legal frameworks differ sharply as well. In the US, property rights are relatively straightforward, and mortgage laws are clearly defined. In many countries, though, non-residents face restrictions on owning land or are limited to specific zones.
In places like the UAE or parts of Asia, foreign buyers can only purchase leasehold properties in designated areas. These limitations don’t exist in the US, so it’s essential to understand the rules in your target country before signing agreements.
Interest Rates and Fees
Interest rates also vary widely. US loans often benefit from competitive rates thanks to the backing of government-sponsored entities. International mortgages may carry higher interest rates, especially if you’re a non-resident, as lenders view these loans as higher risk.
In addition, you may encounter extra fees abroad, including translation costs, legal reviews, and cross-border tax assessments. These can add up quickly and should be factored into your overall budget.
Key Takeaways
The biggest takeaway is that while US loans offer predictability, international mortgages are influenced by local rules, currencies, and property restrictions. You’ll need to prepare for higher deposits, possible legal hurdles, and currency risks. At the same time, buying abroad can open unique investment opportunities if you understand the process and secure the right support.
If you’re thinking of expanding your property portfolio overseas, take time to learn the rules in your chosen country. Careful preparation will help you avoid pitfalls and move with confidence.












