In 2024, regulators levied roughly USD 4.6 billion in corporate penalties — with ninety-five percent from U.S. agencies, according to research from Fenergo highlighted by Corporate Compliance Insights. Those fines drain profit, stall strategy, and rattle investors.
A proactive legal-risk management framework can reverse those losses. By mapping hazards, setting guardrails, and automating follow-through, we let leaders chase growth without costly surprises.
This guide walks you through five fast steps, highlights tech that ends spreadsheet chaos, and links to an independent GRC-software buyer’s guide.
Ready to turn compliance from cost center into competitive edge? Let’s begin.
Step 1. Establish Scope and Secure Leadership Commitment
Clarify your scope and objectives
Map the borders first. Decide whether your legal-risk management framework will cover the entire enterprise or focus on a slice, such as sales and procurement. Write that boundary in plain language and circulate it early.
Spell out the five core legal-risk buckets most companies face: regulatory compliance, contract performance, litigation, data privacy, and intellectual-property disputes. Keeping the list visible stops scope creep before it starts.
Tie every objective to growth. “Avoid fines” is table stakes; “open two new markets next year by meeting local compliance rules” wins budget and attention.
Share the one-page scope with leaders and invite pushback now. Each late edit drains time and goodwill.
Gauge your current maturity
Start with a snapshot. Score how your business handles risk today using a four-level scale: reactive, basic, repeatable, or proactive.
Add external context. PwC’s 2025 Global Compliance Survey found that while a majority of companies are investing in compliance technology, 77% stated that increasing compliance complexity has negatively impacted growth areas. Share this benchmark so leaders see the gap.
Bring the score to life with evidence. When was the last data-privacy audit? How was the biggest contract negotiated? Concrete stories beat spreadsheets and reveal gaps faster, and the best GRC solutions now surface those stories automatically by running more than 1,200 continuous checks across 375 integrations.
Capture the findings in plain language and store them in your risk register. A clear baseline turns next quarter’s progress into a measurable win.
Win executive sponsorship and assign ownership
Book a 30-minute briefing with your CEO, CFO, or General Counsel, the leader who shapes culture. Lead with numbers they recognize:
- The DOJ’s Compensation & Clawback Pilot Program, a three-year initiative started in March 2023, offers a dollar-for-dollar fine reduction when companies withhold bonuses from culpable staff.
- ITIC’s 2024 survey finds that an hour of unplanned downtime now costs large firms USD 300,000 or more.
Then show the upside: a documented framework can cut contract cycle time, accelerate new-market launches, and reassure investors during diligence.
Assign a single executive owner, often the General Counsel, and a cross-functional steering group. Public accountability converts polite nods into funding and signals across the company that legal risk has a permanent seat at the table.
Align with enterprise risk appetite and strategic goals
Start with the numbers. Gartner reports that 42 percent of companies still lack a formal risk-appetite statement, a gap that leaves decisions open to guesswork. Meet with your finance and strategy leads to set dollar and time limits everyone can defend:
- Maximum contract liability per deal
- Acceptable regulatory fine exposure when entering a new market
Write the thresholds in one plain-language paragraph, then link each legal objective to a live initiative. The high-growth SaaS unit, for example, trades a five-percent liability cap for speed, so fallback clauses stay lean. The banking subsidiary, under heavier scrutiny, sets the cap at one percent and adds quarterly audit trails.
When appetite and objectives align, teams view legal guardrails as a navigation system, not a brake. Momentum follows.
Plan resources, talent, and technology early
Vision without funding stays on the whiteboard. Build a lean budget around three essentials:
- People. Staffing levels vary significantly with company size. According to the 2024 ACC Law Department Management Benchmarking Report, companies with less than $1B in revenue have a median of 4 legal team members, while those exceeding $20B in revenue have a median of 158.
- Training. Gartner research emphasizes that investing in robust training and awareness is a critical component of managing risk, as human error remains a significant factor in security incidents.
- Technology. According to a 2021 Gartner forecast, legal-tech spending was projected to reach 12 percent of in-house budgets by 2025, a threefold increase from 3.9% in 2020. Short-list GRC systems with our independent buyer’s guide, pilot one unit, then scale.
Record these allocations in your project charter. Clear dollars, names, and timelines prevent mid-stream stalls and keep momentum rolling.
Step 2. Identify and Prioritize Legal Risks
Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment
With leadership on board, move from vision to visibility. Aim for a panoramic scan of every legal landmine in your daily operations.
- Tour the workflow. Sit in on contract negotiations, product-launch scrums, and customer-support calls. Each touchpoint can hide missed clauses, privacy gaps, or warranty promises that outpace reality.
- Interview the front line. Ask Finance for its three largest invoice disputes, HR for recurring employee claims, and IT for the worst-case data-loss scenario. Stories surface risks no template can show.
- Capture wide, then score later. A 2025 study by Baker Tilly and the Internal Audit Foundation found that 60 percent of organizations still log risks in basic documents, and only 21 percent use a GRC platform. Log every exposure in your system of record; breadth now means fewer shocks later.
Skip ranking for now; simply record what you find in plain language. A complete inventory turns the next step, prioritization, into a data-driven exercise instead of a guessing game.
Look both inside and out for risk sources
Internal slip-ups and external shocks carry equal weight. Start inward:
- Are policies followed or filed away?
- Do standard templates govern every contract, or does each deal begin in Google Docs?
Next, scan the horizon. Cybersecurity and data privacy now rank as the top global dispute risks; 45 percent of in-house counsel place them first in Baker McKenzie’s 2025 Global Disputes Forecast. Add patent trolls, new privacy laws, and geopolitical shifts that can rewrite supply agreements.
Track these five recurring categories in a living checklist you review each quarter:
- Regulatory compliance failures
- Contract breaches or vague terms
- Data-privacy lapses
- Employment and labor disputes
- Intellectual-property claims
Regular review anchors conversations, jogs memories, and keeps the list in step with a changing business.
Estimate likelihood and impact, then rank the critical few
Move from stories to scores. For each risk, ask two questions: How likely is it? How costly will it be if it happens? Use a simple three-point scale — high, medium, or low — to stay quick.
Plot the answers on a heat map. In most organizations, a small slice of risks drives most losses. The Pareto principle shows that 20 percent of causes can create up to 80 percent of effects, according to BetterExplained. Circle that red zone and fund it first.
Document everything in a living risk register
Give each risk its own row in your GRC tool: owner, likelihood, impact, controls, and next review date. When a risk changes color, update the register so dashboards and reports stay aligned. Treat the file as a shared workspace; short, regular notes beat once-a-year rewrites.
Step 3. Design the Legal Risk Management Framework
Anchor your approach to a trusted standard
Eighty percent of large enterprises already anchor their risk programs to ISO 31000 or COSO ERM. The 2024 State of Trust Report from Vanta shows that teams lose eleven working weeks each year to manual security-compliance tasks; layering SOC 2 compliance software like Vanta onto the chosen framework automates evidence collection and continuous control monitoring, turning policy into practice and giving those weeks back.
ISO 31000 reduces risk work to five verbs: establish context, assess, treat, monitor, and review. That cadence mirrors the five steps in this guide. COSO’s ERM cube covers the same ground and also adds strategy and performance lenses, which helps during board discussions.
Choose one framework, translate its terms into your culture, and add a one-page cross-walk in your playbook so directors can see how each article step maps to the chosen clauses.
Define roles, responsibilities, and governance
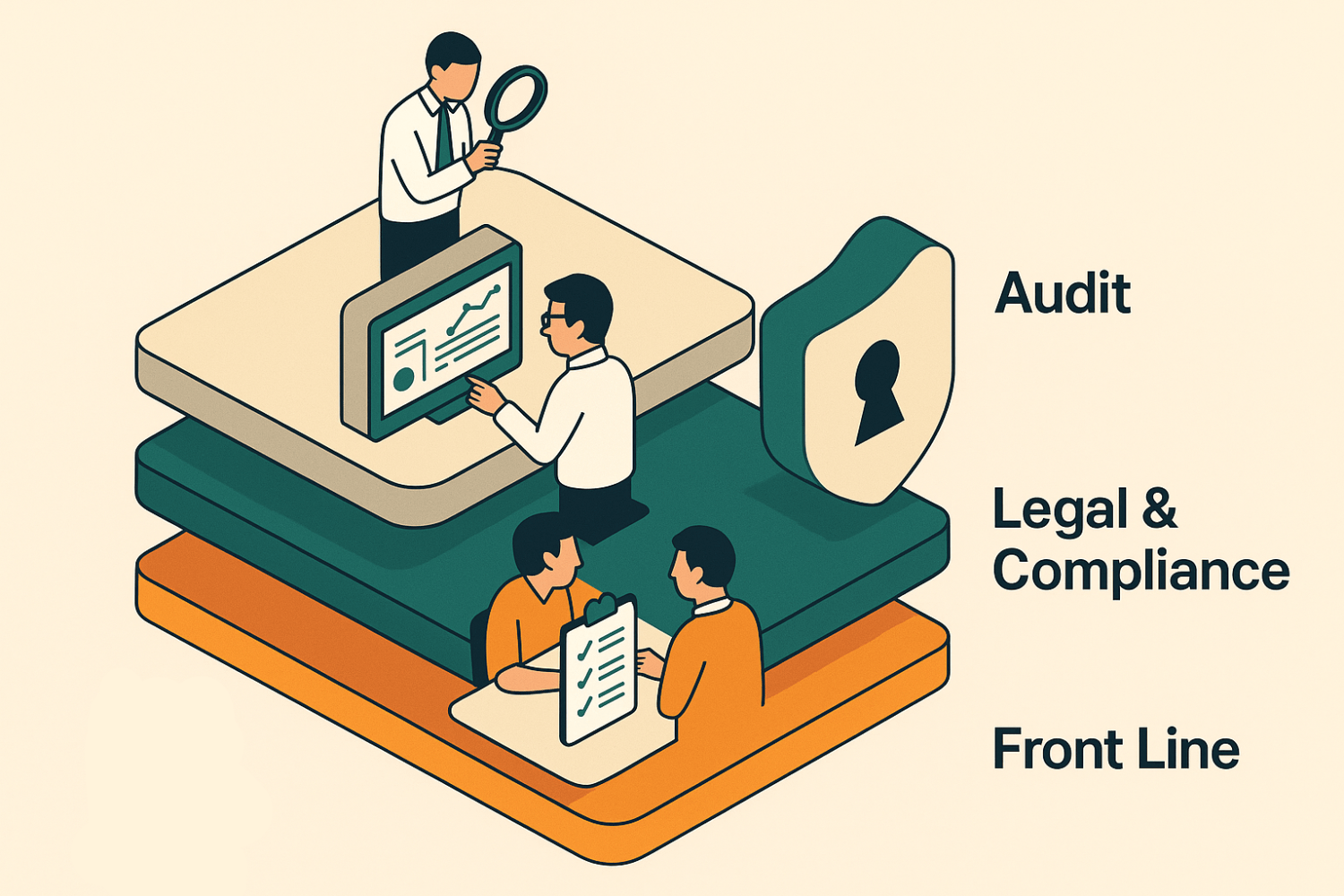
Picture three lines of defense, a structure endorsed by the Institute of Internal Auditors:
- Front line: business managers who draft contracts and handle customer data.
- Legal and compliance: build guardrails, track metrics, and coach the front line.
- Audit or an independent reviewer: test the system and report gaps.
List actual names in a one-page RACI chart. Clear ownership speeds action, while missing names cause confusion and control failure.
Combine policies, processes, and practical controls
Policies set the rule, processes detail the steps, and controls prove they happened. Apply the trio to every high-risk item in your register.
- Regulatory compliance:
- Policy – obey applicable laws
- Process – run a quarterly statute scan, assign owners, and schedule training
- Control – attendance logs, signed attestations, and system checks
- Contracts, data privacy, and employment:
- Policy – follow approved templates and privacy standards
- Process – route each document through your contract-lifecycle or data-protection workflow
- Control – version history, access logs, and completion reports
Embedding controls in daily workflows keeps risk work alive and out of binders.
Set risk thresholds and escalation criteria
Create bright-line triggers for every high-impact area:
- Contract disputes above USD 100,000
- More than two failed login attempts per 1,000 users in a day
- Compliance-training completion below 95 percent
When a trigger fires, the front-line owner alerts Legal within 24 hours. If unresolved after 48 hours, the risk champion briefs the CFO, and severe breaches go directly to the board. Rehearse the ladder in tabletop drills so no one hesitates when alarms ring. Clear numbers end debate and get the right people involved before cost or reputation takes a hit.
Integrate with enterprise risk-management efforts
Integrating legal risk into the main Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) dashboard is a common challenge, often leaving a visibility gap for leadership. A global risk survey from the ERM Initiative at NC State University found that many organizations still struggle to fully link risk oversight with strategic implementation. That gap slows response times on emerging issues. Connect your register to the same system Finance, Operations, and IT use so everyone reads a single heat map.
Join existing risk committees rather than creating a standalone legal council. When product teams plan a new-market launch, you can advise on licensing rules; when Procurement flags geopolitical tension, you add force-majeure and jurisdiction insights.
The payoff is mutual: Legal sees strategy sooner, and the business gains a clear view of downstream exposure. Over time, conversations shift from gate-keeping to goal-keeping, and risk thinking becomes part of daily decision-making.
Step 4. Implement Controls, Training, and Tools
Roll out risk-mitigation measures
Move from plans to action. For each red-zone risk, choose one treatment: avoid, mitigate, transfer, or accept, and then set a clear deadline and owner.
- Data-privacy exposure: Mitigate by restricting access rights, encrypting customer data, and running quarterly audits.
- Contract risk: Transfer by adding indemnity clauses and verifying that insurance riders cover the full liability cap.
- Non-core litigation: Avoid by exiting the product line and archiving legacy obligations.
Track every task in your GRC platform and show status on a single dashboard. You give leadership a real-time view of progress, and owners receive automated nudges until each control closes.
Educate and train stakeholders
Controls collapse if people lack context. Build short, role-focused sessions:
- Sales learns how a missing signature voids revenue.
- Engineers test the difference between anonymized and merely masked data.
- Managers run a five-minute checklist before approving third-party contracts.
Keep the program continuous. A 2025 benchmark from KnowBe4 found that monthly security-awareness training reduced phishing-click rates by 86 percent after one year across 62,000 organizations. Gartner reports that embedding controls in the workflow lowers missed obligations by 58 percent.
Set a target of at least 95 percent completion each quarter, tracked in your GRC platform. Send automatic reminders and log attendance so auditors see a clean record and laggards receive prompts.
Keep lessons conversational. Live demos, quizzes, and real anecdotes stick better than slide decks. Over time, you handle fewer emergency calls and see more issues resolved at the front line, exactly where a mature framework expects them.
Leverage technology and tools
Manual trackers buckle under real-time pressure. Gartner projects that legal-tech spending will reach 12 percent of in-house budgets by 2025, triple the 2020 level. A modern GRC platform centralizes obligations, controls, and due dates, while dashboards flag delinquent tasks and audit trails log every click.
Start small. Load one workflow — contract approvals — and measure the win. An Ironclad 2024 CLM study found that cycle time dropped 36 percent after automation. Early success fuels appetite to expand into policy attestations and regulatory-change monitoring. With all data in one hub, slicing reports by unit, risk theme, or control status takes seconds, not days.
Implement reporting mechanisms
Issue a monthly one-page report that pairs narrative with numbers. Busy executives act on lines like “Contract risk dropped two points after the clause-library rollout.” A 2024 McKinsey study found that teams using real-time dashboards cut issue-resolution time by 30 percent.
Between reports, route hotline and portal alerts straight into your GRC queue so near-misses become early fixes. Fast signals tighten controls before damage spreads.
Test and refine controls
Paper-perfect controls often fail in the wild. Schedule realistic drills such as a mock regulator audit, surprise subpoena, or rogue contract red-line, and time how quickly owners locate documents, follow the escalation ladder, and close gaps.
ISACA recommends tabletop exercises at least once a year, while high-risk sectors often run them every six months. After each drill, debrief within 24 hours. Capture what slowed the response and tweak the checklist while memories stay fresh; simple fixes such as renaming a folder or shortening a form can cut retrieval time by minutes that matter during a real incident.
Run the drill again six months later to keep skills sharp and prove the fix worked. Regular testing turns your framework into a living system that improves every cycle.
Step 5. Monitor, Review, and Continuously Improve
Keep a constant pulse on key risks
Only 35 percent of organizations use real-time risk dashboards, according to the Zipdo 2025 Risk-Management Report. Bridge that gap by routing KRIs from contract systems, security logs, and your finance ERP into a live board.
Hold a 30-minute huddle each month. Owners arrive with numbers, flag anomalies, and log actions in the register.
Automate alerts for any metric that nudges its threshold. A spike in vendor disputes triggers email notifications to Procurement and Legal the same day, not after the quarterly deck. Fast signals enable fast fixes.
Celebrate near-misses caught early. Dashboards turn silent threats into solved problems.
Schedule regular framework reviews and audits
Dashboards cannot judge themselves. Run a full health check each year. Compare current scores with last year’s baseline, then invite an internal audit or independent firm to probe deeper. Capture lessons and fold them into next year’s roadmap so your framework evolves with the business.
Learn from incidents and near-misses
The window for learning closes fast. ISACA’s 2023 crisis-response guide recommends finishing incident reviews within 48 hours to prevent knowledge loss and recurrence. Gather the players, map the timeline, and answer three questions: What slipped? Why? How can we catch it sooner next time?
Log the answers in your risk register and assign an owner. Aim for 100 percent of recordable incidents to receive a post-mortem.
Close the loop with a monthly “risk wins and learns” email, one paragraph per lesson. Quick, candid summaries spread insight across teams and build a speak-up culture where near-misses are celebrated, not buried. Over time, those near-misses become the cheapest training you buy.
Adapt to emerging risks and trends
Gartner’s 2025 Legal-Risk Hot Spots report ranks generative AI, ESG disclosure, and geopolitics as the top three threats; companies that react late face a 40 percent jump in incident costs on average. Reserve one hour each quarter for a horizon scan: regulatory updates, landmark rulings, and tech breakthroughs. Compare every finding with your risk register.
If you spot an uncharted exposure, create a draft entry within 24 hours, assign a temporary owner, and outline a control concept. Speed beats perfection.
When a pattern appears in two consecutive scans, fold it into policy, training, and dashboard metrics. Treat change as a normal sprint, not a panic drill, and your framework stays future ready instead of “we never saw it coming.”
Communicate and report effectively
Risk data needs a story. Convert metrics to outcomes: “Contract risk fell 0.12 points after the template rollout; average negotiation time dropped four days.”
Keep each update to one page with the same headings every cycle. Pair the narrative with a traffic-light chart that leaders can digest in 90 seconds. Yellow sparks questions, and red triggers action.
FAQ
What is a legal-risk management framework? A structured, repeatable system for identifying, assessing, treating, and monitoring legal risks so the business can grow with fewer surprises.
How is it different from general compliance? Compliance meets specific rules; a legal-risk framework goes broader — linking risks to strategy, assigning owners, and tracking controls across the business.
Which standard should we use — ISO 31000 or COSO ERM? Either works. Pick one, translate its terms to your culture, and create a one-page crosswalk so leaders see how your process maps to the standard.
What tools do we actually need? Start with a central risk register (a GRC platform or disciplined spreadsheet), policy attestation tracking, and basic dashboarding. As you scale, add contract lifecycle, regulatory-change, and incident workflows. (Evaluate options with an independent buyer’s guide.)
How do we measure success? Track a small set of KPIs: % of high-risk items with active treatments, training completion, control test pass rate, cycle time (e.g., contract approvals), and incident/near-miss trends over time.
Conclusion
Culture follows example. Deloitte’s 2024 Global Risk Survey found that organizations running leadership “story-sharing” sessions cut near-miss rates by 26 percent. Host a quarterly town hall where executives share wins and lessons.
Bake ownership into daily work: Sales cannot close a deal until the checklist shows green, and product launches wait for privacy sign-off. Set a target of 95 percent of deals passing first-time compliance checks, and publish the score each month.
Recognize proactive behavior. Applaud the engineer who spots an outdated clause or the HR partner who flags a training gap. Small acknowledgments stack up until “legal risk” becomes “our risk.”












